The Science Behind Coffee Grounds as Fertilizer
using coffee grounds as fertilizer for your pineapple plants can offer a range of benefits, contributing to their health, vitality, and even fruit production.
Before we delve into the specific advantages for your pineapple plants, it’s crucial to understand why coffee grounds are considered a beneficial soil amendment. Their magic lies in their unique composition and the way they interact with the soil environment.
Nutrient-Rich Profile: A Feast for Plants
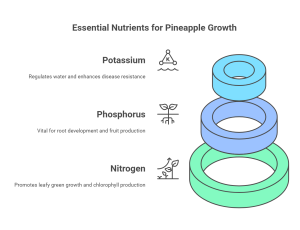
Coffee grounds are like a treasure chest of essential nutrients that plants crave. Here’s a breakdown of the key players:
- Nitrogen (N): This element is the powerhouse behind leafy green growth, promoting vigorous foliage development in pineapples. Nitrogen is essential for the production of chlorophyll, the pigment that gives plants their green color and enables them to perform photosynthesis.
- Phosphorus (P): Crucial for root development, flowering, and fruit production, phosphorus is vital for overall pineapple plant health and productivity. Phosphorus strengthens roots, enabling them to efficiently absorb water and nutrients from the soil. This is especially important for pineapple plants, which have relatively shallow root systems.
- Potassium (K): This nutrient plays a key role in water regulation, disease resistance, and overall plant strength, helping your pineapples thrive even in challenging conditions. Potassium helps regulate the opening and closing of stomata, tiny pores on leaves that control water loss through transpiration. This is crucial for drought tolerance and overall plant resilience.
Beyond these primary nutrients, coffee grounds contain a supporting cast of micronutrients, including magnesium, calcium, and trace elements. These contribute to a well-rounded nutritional profile, fostering robust growth and development.
The pH Factor: Balancing Acidity for Optimal Growth
Coffee grounds are naturally acidic, with a pH typically ranging from 6.5 to 6.8. This acidity can be beneficial for pineapple plants, which prefer slightly acidic soil conditions (ideally between 4.5 and 5.5). The acidity of coffee grounds can help lower the pH of alkaline soils, making certain nutrients more accessible to pineapple plants.
It’s essential to use coffee grounds in moderation, as excessive acidity can negatively impact soil health and nutrient availability. while pineapple plants prefer slightly acidic soil, excessively acidic conditions can hinder their growth.
Maintaining the right pH balance is crucial for optimal nutrient uptake. Regularly testing your soil pH and adjusting with amendments like lime (to raise pH) or sulfur (to lower pH) will help you create the ideal environment for your pineapples to flourish.
Benefits of Coffee Grounds for Pineapple Plants
Now that we’ve covered the scientific basics, let’s explore how these properties translate into tangible benefits for your beloved pineapples:
A Nitrogen Boost for Lush Growth: Fueling Foliage Development
As mentioned earlier, nitrogen is crucial for healthy leaf development. Pineapple plants are known for their striking, sword-shaped leaves, and providing them with an adequate nitrogen supply is key to maintaining their vibrant green color and promoting overall growth.
Coffee grounds, with their relatively high nitrogen content, can provide that extra boost, leading to larger leaves and a more robust plant.
This nitrogen boost is especially beneficial during a pineapple plant’s early stages of growth when it’s focusing on developing a strong foundation of leaves.
Adequate nitrogen supply during this critical phase ensures that your pineapple plant has the building blocks it needs to develop a healthy and productive crown.
Soil Aeration and Drainage: Creating a Breathable Environment
Pineapple plants thrive in well-drained soil, and coffee grounds can play a significant role in improving soil structure. Think of coffee grounds as tiny sponges that enhance aeration and drainage.
They create air pockets within the soil, allowing roots to breathe easily and preventing waterlogging, which can lead to root rot and other problems.
Imagine the difference between trying to breathe through a straw versus breathing freely in open air. That’s essentially what good soil aeration does for your plants! When soil is compacted, it restricts root growth and limits access to oxygen and water.
This is detrimental to pineapple plants, as their roots need a constant supply of both to thrive. The addition of coffee grounds helps loosen up compacted soil, improving its structure and allowing for better water infiltration and air circulation.
Microbial Activity Boost: Fostering a Thriving Soil Ecosystem
A thriving soil ecosystem is teeming with beneficial microorganisms that contribute to plant health in countless ways. These microbes break down organic matter, releasing nutrients in a form readily available to plants, suppress plant diseases, enhance nutrient cycling, and improve soil structure.
Coffee grounds act as a food source for these microbes, encouraging their growth and activity. This increased microbial activity translates into a healthier soil environment overall, leading to stronger and more resilient pineapple plants.
Think of it as fostering a bustling city beneath the surface, with microbes working diligently to provide your pineapple plant with everything it needs to flourish. A diverse and abundant microbial population is essential for nutrient cycling. Microbes break down organic matter, such as fallen leaves or added compost, into simpler compounds that plants can easily absorb.
Coffee grounds, being organic matter themselves, contribute to this cycle, providing a food source for microbes and enhancing the overall nutrient availability for your pineapple plant.
How to Use Coffee Grounds for Pineapple Plants: Application Methods
Now that you understand the “why,” let’s move on to the “how.” There are several ways to incorporate coffee grounds into your pineapple plant care routine:
1. Direct Application: A Simple Approach
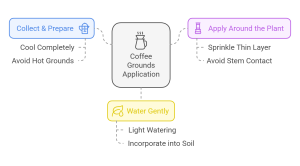
This method is as straightforward as it sounds:
Step-by-Step Guide to Direct Application
- Collect & Prepare: Gather your used coffee grounds and allow them to cool completely. Avoid using hot coffee grounds, as they can harm your plants. The high temperature of freshly brewed coffee grounds can damage plant roots and beneficial microbes in the soil. Allowing them to cool ensures that they won’t negatively impact your pineapple plant.
- Apply Around the Plant: Sprinkle a thin layer (about half an inch) of coffee grounds onto the soil around your pineapple plant, avoiding direct contact with the stem. Applying coffee grounds directly to the stem can create a moist environment that attracts pests or diseases. Distributing them evenly around the drip line of the plant ensures that the nutrients are accessible to the roots as they grow outwards.
- Water Gently: Water the area lightly to help the coffee grounds settle into the soil and begin releasing their nutrients. Watering helps to incorporate the coffee grounds into the soil and prevents them from forming a barrier on the surface.
2. Composting with Coffee Grounds: The Gift that Keeps on Giving
Composting is an excellent way to recycle kitchen scraps and yard waste while creating a nutrient-rich amendment for your garden. Coffee grounds, with their nitrogen content, are a valuable addition to the compost pile. They provide a good balance to carbon-rich materials like dried leaves.
Composting Basics: From Kitchen Scraps to Garden Gold
- Balance is Key: Aim for a mix of “green” materials (like coffee grounds) and “brown” materials (like dried leaves or shredded paper) to achieve the right carbon-to-nitrogen ratio. This balance is crucial for efficient decomposition. A good rule of thumb is to use a ratio of 2:1, brown materials to green materials.
- Keep it Moist: Maintain a damp (not soggy) environment in your compost bin to promote decomposition. Regularly check the moisture level of your compost pile. It should feel like a wrung-out sponge. Too dry, and decomposition slows down; too wet, and it can become anaerobic and smelly.
- Turn Regularly: Aerate the compost pile by turning it regularly to ensure even decomposition. Turning your compost pile every week or two helps to distribute heat evenly, provides oxygen to the microbes, and speeds up the decomposition process.
Once the composting process is complete, you’ll have a rich, crumbly compost that you can mix into the soil around your pineapple plants, providing a slow and steady release of nutrients. Finished compost should have an earthy aroma and a crumbly texture.
3. Making Coffee Ground Tea: A Nutrient-Packed Elixir
For those who prefer a more concentrated approach, coffee ground tea is a fantastic option:
Brewing Up Nutrient-Rich Tea for Your Pineapple Plant
- Steep & Strain: Steep used coffee grounds in water for a few days, allowing the nutrients to leach into the water. Then, strain the mixture through cheesecloth or a coffee filter to remove the solid coffee grounds.
- Dilute & Apply: Dilute the coffee ground tea with water (a 1:4 ratio is a good starting point) and use it to water your pineapple plants. Avoid applying undiluted coffee ground tea, as it can be too strong for plants and may burn their roots.
This method provides a quick and effective way to deliver nutrients directly to the roots. Coffee ground tea is particularly beneficial during the growing season when your pineapple plant requires a consistent supply of nutrients.
Best Practices for Using Coffee Grounds: Tips for Success
While coffee grounds offer numerous benefits, like any good thing, moderation and proper application are crucial.
Frequency and Quantity: Less is More
Overdoing it with coffee grounds can backfire, leading to nutrient imbalances or even harming your plants. A general guideline is to apply a thin layer (no more than half an inch) of coffee grounds around your pineapple plant once a month. However, it’s always wise to observe your plant’s response and adjust the frequency and quantity accordingly.
Think of it as offering your pineapple plant a cup of coffee—one cup can be invigorating, but too much can lead to jitters and discomfort. Similarly, a little bit of coffee grounds can go a long way in providing your pineapple plant with the nutrients it needs, but too much can create an imbalance in the soil.
Balancing Soil pH: The Importance of Testing
As we’ve discussed, coffee grounds are acidic, and while pineapples prefer slightly acidic soil, excessive acidity can hinder nutrient absorption. Regularly testing your soil pH is crucial to ensure it remains within the optimal range for pineapple growth (4.5 to 5.5). If your soil becomes too acidic, you can add lime to neutralize it.
Soil pH test kits are readily available at garden centers and online, empowering you to become a soil scientist in your own backyard. Knowing your soil pH is crucial not only for determining if coffee grounds are a suitable amendment but also for understanding the overall health and nutrient availability of your soil.
Seasonal Considerations: Timing is Everything
Just like our own routines change with the seasons, so do the needs of our plants. Spring and summer are the peak growing seasons for pineapples, so that’s when they’ll benefit most from the extra nutrients coffee grounds provide.
During fall and winter, when growth naturally slows down, you can reduce or even stop applying coffee grounds. Over-fertilizing during dormancy can lead to a buildup of salts in the soil, which can be detrimental to plant health.
Avoiding Pitfalls: Common Mistakes and Troubleshooting
While using coffee grounds is generally safe and beneficial, there are a few potential drawbacks to watch out for:
Over-Application: Recognizing the Signs
As with any fertilizer, too much of a good thing can be harmful. Over-applying coffee grounds can lead to:
- Nitrogen Burn: Excess nitrogen can cause leaf tips to turn brown and crispy. This happens because an excessive amount of nitrogen draws water away from the leaf tips, causing them to dry out and die.
- Fungal Growth: The high organic matter content of coffee grounds can encourage fungal growth, especially in humid conditions. Fungi thrive in moist, organic-rich environments. While most fungi are beneficial to soil health, an overabundance can sometimes lead to issues for plants.
- Pest Attraction: Coffee grounds can attract certain pests, such as ants or slugs. These pests are attracted to the moist, decomposing organic matter.
Troubleshooting Issues: Quick Fixes for Common Problems
- Fungal Growth: If you notice signs of fungal growth, such as white mold on the soil surface, reduce the frequency of coffee ground application and improve air circulation around your plant. Ensure your pineapple plant is not sitting in waterlogged soil. Adequate air circulation helps to dry out the soil surface and discourage fungal growth.
- Pest Infestation: Sprinkle diatomaceous earth around your plant to deter crawling insects. You can also set up traps or use natural repellents to keep pests at bay. Diatomaceous earth is a natural powder made from the fossilized remains of diatoms, a type of algae. It works by dehydrating and killing insects on contact. Be sure to choose food-grade diatomaceous earth for use around plants.
Remember, observation is key! Regularly check your pineapple plant for any signs of distress, and adjust your coffee ground application accordingly.
Success Stories & Expert Tips: Inspiration from the Field
Here are some real-life examples of how gardeners have used coffee grounds successfully with their pineapple plants:
Sarah, a backyard gardener in Florida:
“I started adding coffee grounds to my pineapple plant’s soil last year, and I’ve noticed a significant improvement in its growth! The leaves are greener and larger, and it seems to be thriving.”
Sarah’s experience highlights the positive impact that coffee grounds can have on pineapple plant growth. The added nitrogen and other nutrients in the coffee grounds likely contributed to the improved leaf size and overall plant vigor.
John, a horticulturist from Hawaii:
“Coffee grounds are an excellent source of slow-release nitrogen for pineapples. I recommend mixing them into the soil before planting or applying them as a top dressing around established plants.”
John’s expert tip suggests that coffee grounds can be beneficial throughout the life cycle of a pineapple plant. Incorporating them into the soil before planting provides a slow and steady release of nutrients as the plant establishes its root system.
Alternative Fertilization Methods for Pineapple Plants: Exploring Other Options
While coffee grounds are a fantastic addition to your pineapple plant care arsenal, they’re not the only option. Here are some other effective ways to fertilize your pineapples:
Organic vs. Inorganic Fertilizers: Weighing the Pros and Cons
- Organic Fertilizers: Derived from natural sources like compost, manure, or bone meal, organic fertilizers release nutrients slowly, improving soil structure and promoting microbial activity. They are less likely to burn plants and contribute to a healthier soil ecosystem.
- Inorganic Fertilizers: Manufactured chemically, inorganic fertilizers provide a quick nutrient boost but can deplete soil health over time if not used carefully. They can also lead to a buildup of salts in the soil, which can harm plants.
Here’s a quick comparison:
| Feature | Organic Fertilizers | Inorganic Fertilizers |
|---|---|---|
| Nutrient Release | Slow and steady | Quick release |
| Soil Health | Improves soil structure and microbial activity | Can deplete soil health over time |
| Environmental Impact | Generally more environmentally friendly | Can contribute to water pollution |
Supplementary Fertilizers: Providing an Extra Boost
- Fish Emulsion: Rich in nitrogen and other essential nutrients, fish emulsion is a great all-around fertilizer for pineapple plants. It is derived from whole fish or fish parts that have been liquefied and fermented. Fish emulsion is a good source of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, as well as micronutrients.
- Worm Castings: Also known as vermicompost, worm castings are incredibly rich in nutrients and beneficial microbes, promoting healthy plant growth. They are the excrement of worms that have digested organic matter. Worm castings are considered one of the most nutrient-rich natural fertilizers available.
Experimenting with different fertilizers and observing your plant’s response will help you determine the best feeding regimen for your pineapple.
Conclusion: Brewing Success with Coffee Grounds
Incorporating coffee grounds into your pineapple plant care routine can be a rewarding experience. Not only does it benefit your plants, but it also aligns with sustainable gardening practices by reducing waste and closing the loop in your garden.
Remember to apply coffee grounds in moderation, monitor your plant’s response, and test your soil pH regularly to ensure the best possible outcome. By following these tips, you’ll be well on your way to enjoying the fruits (or should we say, pineapples) of your labor!
Additional Resources
- University of Hawaii Extension: https://www.ctahr.hawaii.edu/
- National Gardening Association: https://garden.org/
Have you tried using coffee grounds for your pineapple plants? Share your experiences and questions in the comments below! Let’s continue the conversation and learn from each other’s gardening journeys.


Leave a Reply